Introduction
Mumps is a viral infection that affects the salivary glands, causing swelling and discomfort. While it is less common today due to vaccines, understanding the mumps meaning in Telugu is important for those who want to learn more about this condition. Whether you’re experiencing symptoms or simply want to stay informed, knowing the signs, causes, and treatment options for mumps is essential.
In this blog, we will explore the mumps meaning in Telugu, its symptoms, how it spreads, and what steps can be taken for prevention and treatment. We will also provide insight into how this viral infection is managed in modern healthcare systems and how it can affect both children and adults.
What Is Mumps?
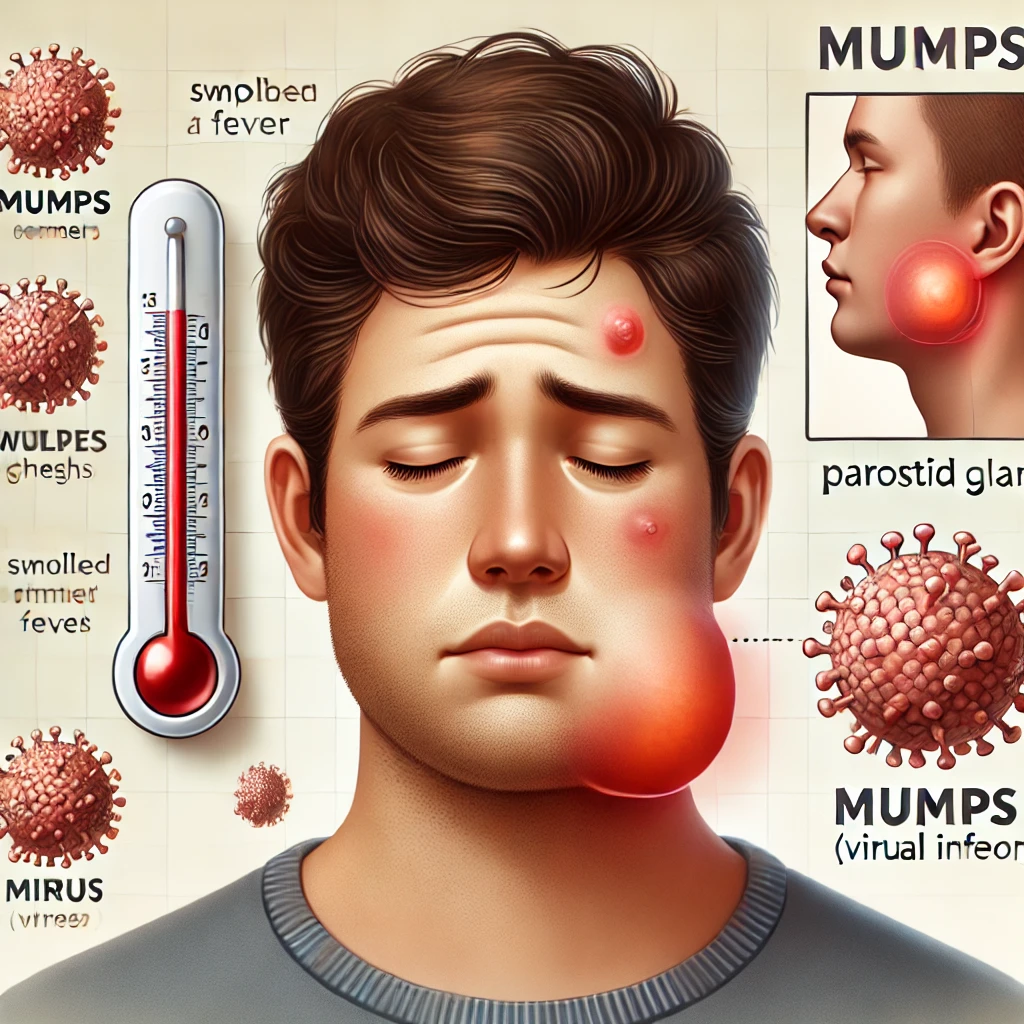
Mumps is a contagious viral infection that primarily affects the parotid glands, which are located near the ears. It causes swelling in these glands, resulting in pain, tenderness, and visible puffiness around the jaw and neck. In some cases, mumps can lead to complications such as hearing loss, meningitis, and inflammation of the testicles (orchitis) in males.
The mumps meaning in Telugu is “మంప్స్” (Mumps), a term used to describe this infection. It is caused by the mumps virus, which is highly contagious and spreads through respiratory droplets, such as when an infected person coughs or sneezes. The virus can also be transmitted through contact with contaminated surfaces or objects.
While mumps was once a common illness among children, the introduction of the MMR vaccine (measles, mumps, and rubella) has significantly reduced the incidence of mumps worldwide. However, outbreaks still occur, particularly in communities with low vaccination rates.
Symptoms of Mumps
The most noticeable symptom of mumps is the swelling of the parotid glands. This can cause the cheeks to puff up, making it look like a person has a “chipmunk” appearance. The swelling is usually painful and can make it difficult to chew or swallow.
Other symptoms of mumps include:
- Fever: A mild to moderate fever is common, especially in the early stages of the infection.
- Headache: Mumps can cause headaches due to the swelling of the glands and the body’s immune response.
- Fatigue: Individuals with mumps often feel tired or weak, as the body fights off the infection.
- Loss of Appetite: Swelling in the mouth and jaw area can make eating uncomfortable, leading to a reduced appetite.
- Sore Throat: The swelling can extend to the throat, causing discomfort when swallowing.
- Pain While Chewing: The discomfort in the parotid glands can make it painful to chew food.
In some cases, mumps meaning in Telugu can also cause more serious complications, such as meningitis (inflammation of the brain and spinal cord lining), orchitis (inflammation of the testicles), or pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas).
How Does Mumps Spread?
Mumps is a contagious disease that spreads easily from person to person. The mumps meaning in Telugu is often associated with transmission via respiratory droplets, which are released when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. Additionally, the virus can spread by touching surfaces or objects that have been contaminated by saliva or nasal secretions from an infected person.
The virus is most contagious a few days before the swelling begins and continues to be contagious for several days after the swelling has started to subside. This makes it difficult to contain the infection, as people may unknowingly spread the virus before they even realize they are infected.
If you are in close contact with someone who has mumps, it’s important to take preventive measures, such as avoiding close physical contact and practicing good hygiene (such as washing your hands regularly).
Prevention of Mumps
The most effective way to prevent mumps is through vaccination. The mumps meaning in Telugu becomes less concerning when individuals are vaccinated, as the MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine provides immunity against the mumps virus. The vaccine is typically given in two doses: the first dose is usually administered at 12-15 months of age, with the second dose given at 4-6 years of age.
In areas where the MMR vaccine is not widely used or where vaccination rates are low, outbreaks of mumps can still occur. In such cases, individuals who are unvaccinated or who have not received the full course of the MMR vaccine may be at a higher risk of contracting the disease.
Apart from vaccination, other preventive measures include:
- Avoiding Close Contact: If someone you know has mumps, try to limit close contact with them, especially if they are showing symptoms like swelling or fever.
- Washing Hands Regularly: Good hygiene practices can help reduce the spread of the virus. Wash your hands frequently, especially after coughing, sneezing, or touching surfaces.
- Covering Coughs and Sneezes: Using a tissue or your elbow to cover your coughs or sneezes can prevent respiratory droplets from spreading in the air.
- Staying Home When Sick: If you are sick with mumps or any other contagious illness, stay home from school or work to avoid infecting others.
Treatment of Mumps
Currently, there is no specific antiviral treatment for mumps. The treatment primarily focuses on relieving symptoms and supporting the body’s immune response to the virus. Here are some common treatments for mumps:
- Rest: Rest is crucial to help the body recover and build up immunity against the virus.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help alleviate pain and reduce fever. Always follow the dosing instructions and consult a healthcare provider if necessary.
- Hydration: It’s important to stay hydrated, especially if you have a fever or a sore throat. Drinking plenty of fluids can help prevent dehydration.
- Cold Compresses: Applying cold compresses to the swollen areas of the face can help reduce discomfort and swelling.
If you experience complications from mumps, such as meningitis, orchitis, or pancreatitis, additional medical treatment may be required. In some cases, hospitalization may be necessary to manage these complications.
Complications of Mumps
Although most people recover from mumps without any serious issues, there are certain complications that can arise, particularly in adults. These include:
- Meningitis: Inflammation of the brain and spinal cord lining, which can cause severe headaches, neck stiffness, and sensitivity to light.
- Orchitis: Inflammation of the testicles, which can cause pain, swelling, and discomfort in males. In rare cases, orchitis can lead to infertility.
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas, which can cause abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
- Deafness: Mumps can sometimes lead to hearing loss, particularly if the infection affects the inner ear.
Although these complications are rare, they can be serious, and prompt medical attention is important if symptoms worsen or new symptoms develop.
Mumps in Adults vs. Children
While mumps is more commonly associated with children, adults can also get infected, particularly if they have not been vaccinated. In fact, mumps meaning in Telugu may be more severe in adults than in children. The risk of complications, such as orchitis and meningitis, is higher in adults.
For children, mumps usually resolves on its own with minimal complications, especially when they are vaccinated. However, if left untreated in adults, the infection can lead to prolonged symptoms and more serious health issues.
Conclusion
Understanding the mumps meaning in Telugu is key to recognizing the symptoms, preventing the infection, and seeking appropriate treatment. While mumps is less common today due to widespread vaccination, it’s important to continue practicing good hygiene and vaccination practices to prevent outbreaks. If you or someone you know develops symptoms of mumps, seek medical attention to manage the symptoms and prevent complications. By staying informed and taking the right precautions, you can protect yourself and your loved ones from this contagious viral infection.